Flowchart of the Program
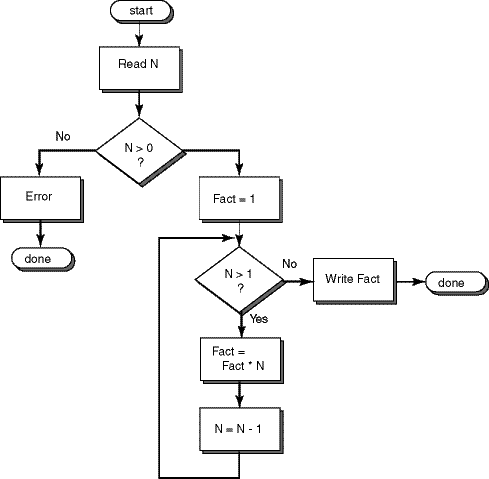
Another way to do this is to use N as the counter, and count it down until it reaches 2, so its values are: 5, 4, 3, and 2. These values are multiplied together one by one. There is no need to multiply by 1, so the loop's condition is N > 1.
Here is a flowchart of the program. It tests if N is a correct value before it calculates N!
This is somewhat trickier logic than previous programs have used. Study the flowchart until you see how it works. Don't worry about the details of Java (yet!) In fact, the flowchart says nothing about which language the program is written in. The same flowchart could be used for Ada, C, C++, BASIC, FORTRAN, Pascal... and others.